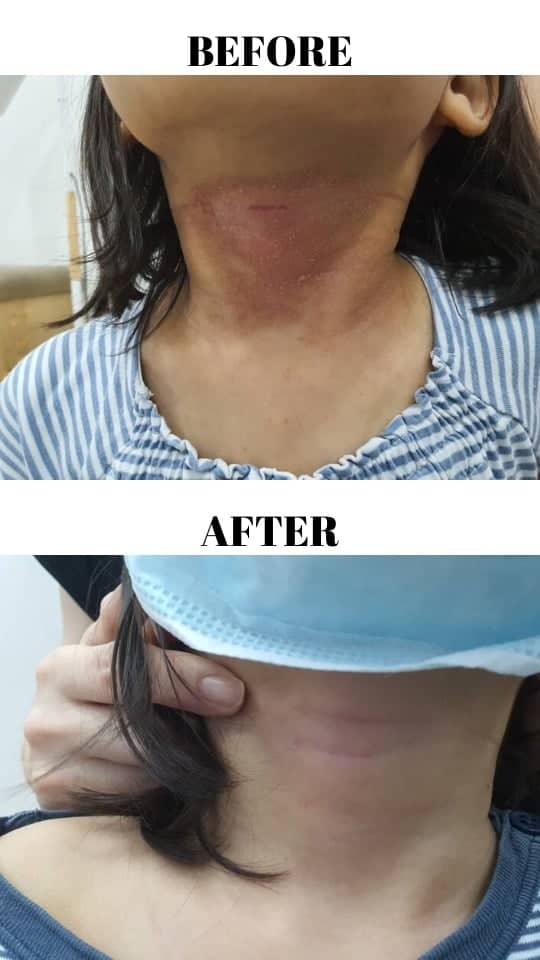
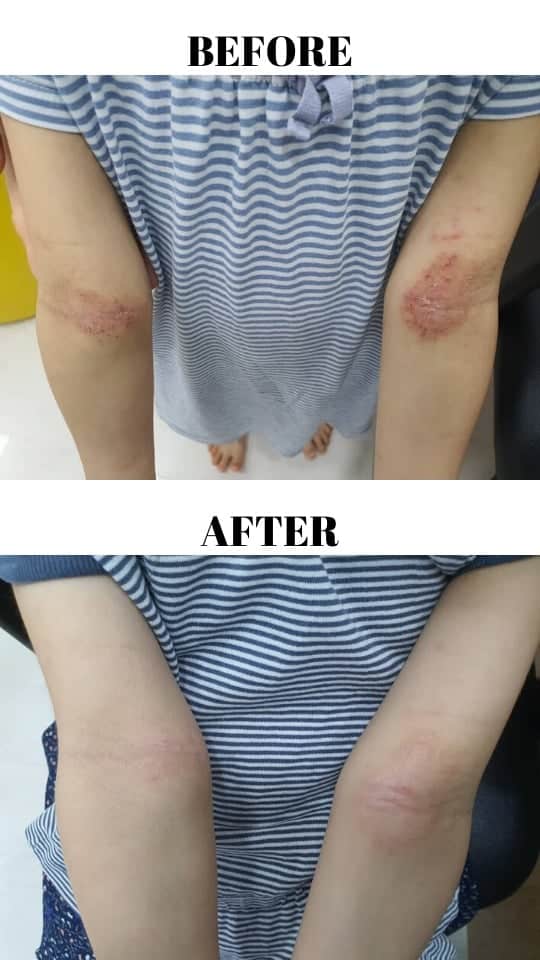
A five-years-old child came to the clinic with the complaint of worsening, spreading skin rash for the past two weeks. On further questioning, this child has underlying eczema since young. Her mother also noticed that her rash appears wet with some yellowish discharge. What could be the reason for this worsening rash?
What is eczema?
Eczema is a common condition in children that usually begins by the age of 5 years. It is characterised by the appearance of skin which is dry, scaly and itchy. Eczema is also known as atopic dermatitis.
What causes eczema?
The cause of eczema is due to a combination of genes and trigger factors. A person with eczema has an over-reactive immune system, that when triggered causes inflammation. It is this inflammation that causes the skin to be red, itchy or painful.
Some people with eczema also have a mutation of the gene responsible for creating filaggrin. Filaggrin is responsible for maintaining a healthy, strong skin barrier. Hence, with the lack of filaggrin, the skin tends to be dry and prone to infection.
What are the causes that can worsen eczema?
✏️ Dry skin
One of the major culprits! When your skin gets too dry, it becomes brittle, scaly, rough and will lead to a flare-up!
➡️ Bathe your child not more than 5-10 minutes in lukewarm water. Then apply thick, fragrance-free moisturiser within 3 minutes of bathing.
✏️ Scratching
Never scratch! Ever! Scratching will only invite more inflammatory cells, worsening the itchiness. This results in the never-ending “scratch-itch” cycle.
➡️ Lightly tap the itchy area, apply anti-itch cream or try a cold impression instead. If the itch is severe, give your child antihistamines.
✏️ Bacterial infection
A sudden worsening or spreading eczema could be due to secondary bacterial infection. In eczema, the dry skin is prone to cracks, providing an opportunity for commensal (normal) skin bacteria to seep in, multiply and cause an infection.
➡️ Any worsening eczema should be evaluated by a doctor for secondary bacterial infection, which is usually treated with an antibiotic cream or oral antibiotics depending on the severity. Infection with fungus (ringworm) or virus (herpes virus) is also uncommon.
✏️ Sweat and saliva
These bodily fluids are skin irritants.
➡️ Gently pat saliva on the cheek with a soft cloth. Rubbing can trigger itchiness. Apply a thin layer of barrier cream like petroleum jelly to prevent contact between saliva and skin.
➡️ Dress your child in loose-fitting 100% cotton clothes and prevent overheating.
➡️ If your air-conditioner is on most of the time, always remember that cold air is drying; hence moisturiser should be applied as frequent as possible.
✏️ Food allergy
Food allergy does not cause eczema but can worsen the skin condition.
➡️Take note of the foods that seem to trigger eczema. In severe food allergies leading to difficulty in breathing, nausea, vomiting or eye swelling, seek medical attention immediately.
➡️ In children with unknown or multiple food allergies, an allergy test may be beneficial to identify the culprits responsible.
Thankfully this unfortunate child made a remarkable recovery after just a week of treatment. ❤️
References:
1. National Eczema Association nationaleczema.org
2. American Academy of Dermatology Association aad.org
3. Pictures posted with verbal consent from mother
Related articles:
https://drjoannchildspecialist.com/lymph-node-in-children/
https://drjoannchildspecialist.com/risks-of-using-baby-powder/
INTERESTED IN PARENTING ARTICLES?
We have the right articles just for you.
“There is no such thing as a perfect parent. So just be a real one.” – Sue Atkins